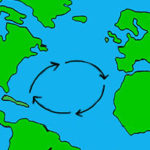
What is the Coriolis effect?
The Coriolis effect is caused by the fact that the earth is a globe that rotates on its axis every day. The speed at which it rotates isn’t the same everywhere on earth. When the earth rotates once every 24 hours, the circle that the earth makes at the North Pole is smaller than the circle at the equator. As a result, the earth turns faster at the equator than at the poles.
The earth’s rotation bends ocean currents
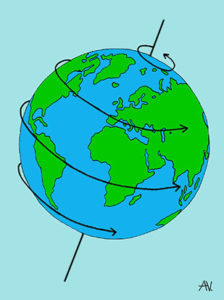
The earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours. The circle it makes is smaller at the poles than it is at the equator. As a result, the earth turns faster at the equator than at the poles.
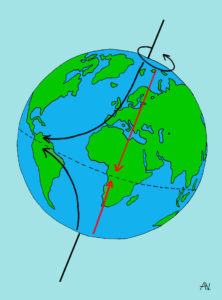
The earth’s rotation makes wind and water currents bend in a specific direction. In the Northern Hemisphere, the bend turns in a clockwise direction, and in the Southern Hemisphere it turns counter-clockwise.
In the Northern Hemisphere, wind and water currents bend in a clockwise direction, and in the Southern Hemisphere they turn counter-clockwise. That is because if the water or wind want to move from north to south, the movement is affected by the speed of the earth’s rotation. When wind or water move from north to south, the rotation of the earth keeps it from moving in a straight line.
Coriolis effect influences ocean surface currents
The wind blows across the surface of the ocean, creating a surface current. Since the wind in the Northern Hemisphere blows in the opposite direction to the wind in the Southern Hemisphere, the currents in the Northern Hemisphere turn in a clockwise direction, and in the Southern Hemisphere they turn counter-clockwise.
More interesting info…